A brand new Epoch Occasions ballot reveals sturdy assist for reforms to the federal Medicaid program, together with work necessities and fraud discount, whereas additionally highlighting deep skepticism about Congress’s skill to implement these adjustments responsibly.
The survey, which garnered 18,369 responses, comes as lawmakers debate a sequence of proposals to rein within the federal authorities’s ballooning Medicaid funds—now exceeding $800 billion a 12 months throughout each federal and state budgets, together with over $600 billion in federal spending alone.
Among the many most hotly debated concepts are lowering the federal share of state Medicaid prices, tightening eligibility guidelines, imposing new work necessities, and capping federal spending per enrollee. These proposals have divided Republican lawmakers, with moderates warning of political backlash from constituents who depend on this system, and financial hawks pushing for aggressive cost-cutting to rein in deficit progress.
Towards this backdrop, the Epoch Occasions ballot provides a snapshot of the place readers stand. By way of each structured survey responses and greater than 10,000 open-ended feedback, the outcomes counsel sturdy assist for focused, accountability-driven reforms—but warning in opposition to sweeping adjustments that might disrupt take care of weak Individuals.
Work Necessities, Waste Discount, and Medicaid’s Increasing Value Footprint
Medicaid at the moment covers over 90 million low-income Individuals by a joint federal–state partnership. Whereas the federal authorities supplies broad oversight and a big share of the funding, states administer this system and decide eligibility guidelines, supplier cost charges, and profit choices.
Program prices have surged—significantly for the reason that Inexpensive Care Act (ACA) expanded eligibility in 2014 to incorporate most low-income adults incomes as much as 138 p.c of the federal poverty degree, no matter parental standing. At the moment, roughly 21 million persons are coated by this enlargement. For these enrollees, the federal authorities covers 90 p.c of the fee, in comparison with between 50 and 77 p.c for conventional Medicaid recipients, relying on the state.
Because of this, federal Medicaid spending has almost doubled over the previous decade, climbing to $614 billion yearly. That progress has sparked mounting concern over long-term fiscal sustainability and ballooning deficits.
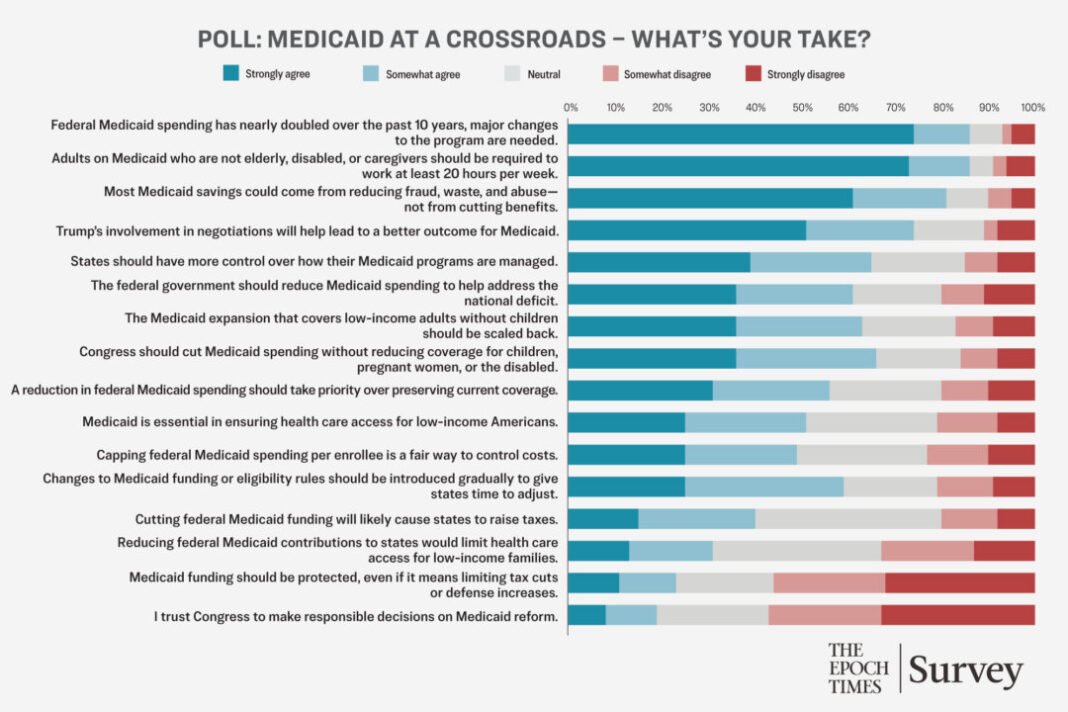
Survey responses from Epoch Occasions readers replicate this concern. Almost three-quarters strongly agreed—and one other 12 p.c considerably agreed—that main adjustments to Medicaid are wanted. Solely 14 p.c expressed opposition or remained impartial, suggesting broad dissatisfaction with the established order and a robust assist for reform.
One reform that has regained momentum is linking Medicaid eligibility to work necessities for able-bodied, non-elderly adults—excluding college students and people caring for dependents.
Throughout President Donald Trump’s first time period, the federal authorities authorized Part 1115 waivers in 13 states that conditioned Medicaid eligibility on assembly work and reporting necessities. Solely Arkansas absolutely enforced this system, which led to over 18,000 enrollees shedding protection earlier than courts intervened.
The Biden administration later withdrew all such waivers, arguing that work necessities undermined the core Medicaid aim of increasing entry to care. However as of April 2025, no less than 11 states are once more looking for federal approval to implement related insurance policies. Georgia stays the one state with an energetic work requirement, after efficiently difficult the waiver withdrawal in court docket.
The Epoch Occasions ballot reveals overwhelming assist for reinstating such insurance policies. When requested whether or not able-bodied adults who will not be aged, disabled, or caregivers must be required to work no less than 20 hours per week to take care of Medicaid eligibility, 86 p.c stated sure—together with 73 p.c who strongly agreed. Simply 9 p.c expressed opposition, and 5 p.c had been impartial—signaling broad public backing for work as a situation for receiving taxpayer-funded advantages.
Epoch Occasions readers seem to see this space as ripe for reform. Slightly than lowering protection or slashing advantages, respondents overwhelmingly favored reducing Medicaid prices by first focusing on inefficiency and abuse. In complete, 81 p.c agreed—together with 61 p.c who strongly agreed—that the most effective path to financial savings lies in lowering fraud and waste, not reducing core advantages. Solely 10 p.c disagreed.
As Republicans huddle in Washington to hammer out a broad fiscal bundle that features Medicaid reforms, Trump’s presence looms massive over the negotiations. He has forged himself as each a funds hawk and a staunch defender of core entitlement applications. Whatever the actions Congress in the end takes, Trump is set to enhance Medicaid, in line with White Home deputy press secretary Kush Desai.
“The Trump administration is dedicated to defending Medicaid whereas slashing the waste, fraud, and abuse inside the program—reforms that can improve effectivity and enhance take care of beneficiaries,” Desai informed The Epoch Occasions in an earlier assertion.
That view is extensively shared by Epoch Occasions readers. When requested whether or not Trump’s involvement would assist produce a greater Medicaid reform consequence, 74 p.c stated sure—together with 51 p.c who strongly agreed. Solely 11 p.c expressed disagreement, underscoring the president’s continued sway over coverage debates.
State Flexibility, Fiscal Tradeoffs, and the Way forward for Medicaid Growth
Whereas survey respondents expressed broad assist for fraud discount and work necessities, the Epoch Occasions ballot additionally revealed extra nuanced views round federal spending ranges and state management. Respondents had been break up on how far Medicaid reforms ought to go—and what tradeoffs they’d settle for.
Fiscal conservatives argue these adjustments would encourage funds self-discipline and long-term sustainability, whereas moderates say they may pressure states to both increase taxes or cut back protection. This rigidity was mirrored within the Epoch Occasions ballot.
A strong 65 p.c of readers stated they favor giving states extra authority over how Medicaid is managed—although a sizeable 20 p.c had been undecided, and 15 p.c had been against the concept. This implies broad assist for federalism paired with concern about how states would deal with the added duty.
That divide grew to become extra pronounced when the main focus shifted to federal spending. Whereas 61 p.c of respondents supported lowering Medicaid outlays to handle the deficit, 20 p.c disagreed and 19 p.c had been undecided—signaling that enthusiasm for cuts is tempered by uncertainty about potential fallout.
The strain between accountable stewardship of taxpayer funds and offering government-funded well being take care of the weak is probably most pronounced with regards to the Inexpensive Care Act’s Medicaid enlargement, which prolonged protection to greater than 21 million low-income adults, many with out dependent youngsters. Underneath this enlargement, the federal authorities provides states a beneficiant 90 p.c reimbursement fee, far above the 50–77 p.c typical for conventional Medicaid.
Within the Epoch Occasions ballot, 63 p.c of readers stated they assist rolling again the enlargement, however 20 p.c remained undecided, and 17 p.c opposed the transfer—outcomes that time to the problem’s political sensitivity.
Even amongst these favoring cuts, many respondents drew crimson traces round who must be protected. When requested whether or not Congress ought to cut back Medicaid spending whereas preserving protection for kids, pregnant ladies, and the disabled, two-thirds stated sure. Solely 16 p.c disagreed, suggesting sturdy public assist for reforms that carve out exemptions for essentially the most weak.
The tradeoffs grew to become much more obvious when respondents had been requested if reducing federal Medicaid spending ought to take priority over preserving present protection. A slender majority—56 p.c—stated sure, however 24 p.c had been undecided, and 20 p.c disagreed.
Gradual Reform, Value Caps, and a Disaster of Confidence in Congress
Among the many extra detailed coverage questions within the ballot had been these addressing advanced proposals now on the desk in Washington, together with gradual implementation of reforms, capping federal Medicaid spending per enrollee, and rebalancing the federal-state funding break up.
The responses mirrored a recurring sample all through the survey: whereas readers strongly favor reform, many are cautious about abrupt adjustments that threat disrupting care or overwhelming state methods.
On the core query of Medicaid’s position, simply over half—51 p.c—agreed that this system is important to making sure well being care entry for low-income Individuals. However 21 p.c disagreed, and 28 p.c had been undecided, pointing to a lukewarm consensus amid ongoing debate concerning the scope and objective of this system.
Some of the debated proposals in Washington is the introduction of per-capita caps—fastened federal spending limits for every Medicaid enrollee, listed to inflation. In contrast to the present open-ended construction, during which federal funding rises consistent with state spending, this strategy would constrain future federal contributions no matter state-level price will increase.
Regardless of the projected fiscal advantages of per-capita caps, there was comparatively weak consensus across the coverage amongst readers. Forty-nine p.c agreed that capping federal Medicaid spending per enrollee is a good method to management prices, together with 25 p.c who strongly agreed. In the meantime, 23 p.c opposed the concept, and 28 p.c had been undecided—highlighting vital uncertainty about how such a cap would possibly play out in apply.
Whereas views on spending caps had been combined, there was broader consensus on how any main adjustments must be carried out. A transparent majority—59 p.c—favored a phased rollout of reforms to provide states time to regulate, aligning with CBO warnings that abrupt shifts might pressure states to chop enrollment, cut back supplier funds, or remove non-obligatory advantages.
Nonetheless, many respondents had been not sure how lowered federal assist would possibly influence state funds. When requested whether or not Medicaid cuts would probably result in state-level tax hikes, 40 p.c stated they had been unsure—the most important share of any response class. One other 40 p.c believed tax will increase had been probably, whereas 20 p.c disagreed.
Comparable uncertainty surfaced round entry to care. Simply 31 p.c of readers believed that reducing federal contributions would cut back well being care entry for low-income households, whereas 33 p.c disagreed and 36 p.c had been not sure—making this some of the evenly divided questions within the ballot.
Requested to rank Medicaid relative to different fiscal priorities akin to tax cuts or protection spending, simply 23 p.c of respondents supported defending this system even when it meant scaling again elsewhere. A full 56 p.c opposed shielding Medicaid from cuts in that context, together with 32 p.c who strongly disagreed.
Maybe the clearest message got here in response to a query about congressional management. Solely 19 p.c of readers stated they belief Congress to handle Medicaid reform responsibly, whereas 57 p.c expressed mistrust—together with one-third who strongly disagreed. That credibility hole casts doubt on the prospect of actual reform in Washington.
Reader Proposals: Reduce Fraud, Implement Work Necessities, Tighten Eligibility
Past the structured questions, readers had been invited to counsel one change they’d make to enhance Medicaid. Greater than 10,000 responded, providing a few of the clearest perception into attitudes towards this system.
The most typical theme—by a large margin—was the necessity to crack down on fraud and abuse. Respondents referred to as for stricter eligibility checks, aggressive auditing of suppliers, and legal prosecution of those that exploit the system, whether or not recipients or medical professionals. Many expressed deep frustration that lax oversight permits billions in taxpayer {dollars} to be wasted.
Work necessities had been additionally a prime concern. Hundreds stated able-bodied adults must be required to work, practice, or carry out neighborhood service with the intention to obtain advantages. Medicaid was incessantly described as a brief security internet, not a long-term substitute for employment. A number of respondents advocated time-limited advantages or scaled protection reductions for these unwilling to fulfill primary necessities, particularly for childless adults.
Citizenship and immigration standing additionally featured prominently. Many argued that Medicaid must be restricted to U.S. residents or lawful everlasting residents, with unlawful immigrants categorically excluded. Some referred to as for retroactive audits of enrollment to make sure compliance, citing equity to taxpayers and issues about funding priorities.
Different recurring themes included calls to modernize Medicaid’s outdated expertise methods, simplify eligibility throughout states, and herald private-sector administration practices to scale back inefficiency. A vocal minority questioned whether or not Medicaid ought to stay a federal program in any respect, advocating as an alternative for full state management or privatized alternate options.
Total, readers seem to need Medicaid spending reined in—whereas leaning in the direction of cautious, disciplined reforms over drastic overhauls.