In cybersecurity, precision issues—and there is little room for error. A small mistake, missed setting, or quiet misconfiguration can shortly result in a lot greater issues. The indicators we’re seeing this week spotlight deeper points behind what may appear like routine incidents: outdated instruments, sluggish response to dangers, and the continued hole between compliance and actual safety.
For anybody liable for defending methods, the important thing is not simply reacting to alerts—it is recognizing the bigger patterns and hidden weak spots they reveal.
This is a breakdown of what is unfolding throughout the cybersecurity world this week.
⚡ Risk of the Week
NCA Arrests for Alleged Scattered Spider Members — The U.Ok. Nationwide Crime Company (NCA) introduced that 4 individuals have been arrested in reference to cyber assaults focusing on main retailers Marks & Spencer, Co-op, and Harrods. The arrested people embody two males aged 19, a 3rd aged 17, and a 20-year-old girl. They have been apprehended within the West Midlands and London on suspicion of Laptop Misuse Act offenses, blackmail, cash laundering, and taking part within the actions of an organized crime group. They’re believed to be related to the infamous cybercrime group often known as Scattered Spider, an offshoot of a loose-knit collective referred to as The Com, which is liable for an enormous catalog of crimes, together with social engineering, phishing, SIM swapping, extortion, sextortion, swatting, kidnapping, and homicide.
🔔 High Information
- PerfektBlue Bluetooth Flaws Expose Hundreds of thousands of Autos to Distant Assaults — Cybersecurity researchers have found a set of 4 safety flaws in OpenSynergy’s BlueSDK Bluetooth stack that, if efficiently exploited, might permit distant code execution on thousands and thousands of transport autos from Mercedes-Benz, Volkswagen, and Skoda. “PerfektBlue exploitation assault is a set of essential reminiscence corruption and logical vulnerabilities present in OpenSynergy BlueSDK Bluetooth stack that may be chained collectively to acquire Distant Code Execution (RCE),” PCA Cyber Safety mentioned. Volkswagen mentioned the recognized points solely concern Bluetooth and that neither is car security nor integrity affected. It additionally famous that exploitation of the vulnerabilities is just doable when a number of situations are met concurrently.
- North Korean Hacker Behind Fraudulent IT Employee Scheme Sanctioned — The U.S. Division of the Treasury’s Workplace of International Belongings Management (OFAC) on Tuesday sanctioned a member of a North Korean hacking group referred to as Andariel for his or her position within the notorious distant info expertise (IT) employee scheme. Tune Kum Hyok, 38, is alleged to have enabled the fraudulent operation through the use of foreign-hired IT staff to hunt distant employment with U.S. firms and planning to separate revenue with them. The sanctions mark the primary time a risk actor linked to Andariel, a sub-cluster inside the Lazarus Group, has been tied to the IT employee scheme. “Whereas the Treasury’s announcement marks a proper public affiliation of the Andariel (APT45) hacking group with North Korea’s distant IT employee operation, the connection displays a wider and long-running sample,” Michael “Barni” Barnhart, Principal i3 Insider Threat Investigator at DTEX, informed The Hacker Information.
- Chinese language Hacker Arrested for Silk Hurricane Assaults — A Chinese language nationwide has been arrested in Milan, Italy, for his alleged hyperlinks to a state-sponsored hacking group often known as Silk Hurricane and for finishing up cyber assaults towards American organizations and authorities companies. Xu Zewei, 33, has been accused of being concerned within the U.S. laptop intrusions between February 2020 and June 2021, together with a mass assault spree that leveraged then-zero-day flaws in Microsoft Change Server, a cluster of exercise the Home windows maker designed as Hafnium. Xu, alongside co-defendant and Chinese language nationwide Zhang Yu, are believed to have undertaken the assaults primarily based on instructions issued by the Ministry of State Safety’s (MSS) Shanghai State Safety Bureau (SSSB).
- Risk Weaponize Leaked Model of Shellter to Distributed Stealers — Hackers are exploiting a preferred purple teaming instrument referred to as Shellter to distribute stealer malware and distant entry trojans. The campaigns are believed to have began in April 2025, across the similar time an organization that procured a licensed model of the software program leaked a duplicate on cybercrime boards. “Though the Shellter Mission is a sufferer on this case by mental property loss and future improvement time, different members within the safety house should now deal with actual threats wielding extra succesful instruments,” Elastic Safety Labs mentioned.
- Fortinet Patches Crucial SQL Injection Flaw — Fortinet has launched fixes for a essential safety flaw impacting FortiWeb that might allow an unauthenticated attacker to run arbitrary database instructions on prone situations. Tracked as CVE-2025-25257, the vulnerability carries a CVSS rating of 9.6 out of a most of 10.0. In response to watchTowr Labs, the issue is rooted in the truth that a Bearer token Authorization header in a specifically crafted HTTP request is handed on to an SQL database question with out satisfactory sanitization to ensure that it is not dangerous and doesn’t embody any malicious code. The disclosure comes as Sonar detailed a number of vulnerabilities in Fortinet’s FortiClient (CVE-2025-25251, CVE-2025-31365, CVE-2025-22855, CVE-2025-22859, and CVE-2025-31366) that, when chained collectively, grants an attacker full organizational management with minimal person interplay. CVE-2025-22859 “allows an authenticated attacker to add a saved XSS payload to a Linux-based EMS server,” safety researcher Yaniv Nizry mentioned. “Exploiting this vulnerability, an attacker can manipulate an EMS person into clicking a malicious hyperlink, forcing all registered endpoints to change connection to a malicious EMS server with none interplay from the purchasers. This makes them prone to arbitrary code execution.”
️🔥 Trending CVEs
Hackers are fast to leap on newly found software program flaws – typically inside hours. Whether or not it is a missed replace or a hidden bug, even one unpatched CVE can open the door to critical harm. Beneath are this week’s high-risk vulnerabilities making waves. Overview the checklist, patch quick, and keep a step forward.
This week’s checklist consists of — CVE-2025-47227, CVE-2025-47228 (ScriptCase), CVE-2025-24269, CVE-2025-24235 (SMBClient), CVE-2025-30012, CVE-2025-42963, CVE-2025-42964, CVE-2025-42966, and CVE-2025-42980 (SAP), CVE-2025-52488 (DNN), CVE-2025-44954, CVE-2025-44955, CVE-2025-44957, CVE-2025-44958, CVE-2025-44960, CVE-2025-44961, CVE-2025-44962, CVE-2025-44963, CVE-2025-6243 (Ruckus Wi-fi), CVE-2025-52434, CVE-2025-52520, CVE-2025-53506 (Apache Tomcat), CVE-2025-6948 (GitLab CE/EE), CVE-2025-0141 (Palo Alto Networks GlobalProtect App), CVE-2025-6691 (SureForms plugin), CVE-2025-7206 (D-Hyperlink DIR-825), CVE-2025-32353, CVE-2025-32874 (Kaseya RapidFire Instruments Community Detective), CVE-2025-7026, CVE-2025-7027, CVE-2025-7028, CVE-2025-7029 (Gigabyte UEFI), CVE-2025-1727 (Finish-of-Practice and Head-of-Practice units), and a essential double free vulnerability within the Linux kernel’s pipapo set module.
📰 Across the Cyber World
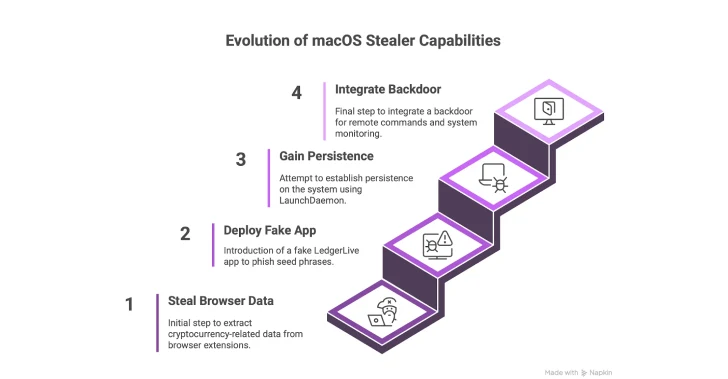
- Atomic Stealer Will get a Backdoor Characteristic — The macOS info stealer often known as Atomic Stealer (aka AMOS) has been up to date with an embedded backdoor to acquire persistent entry to compromised methods. The brand new element permits executing arbitrary distant instructions, gaining full user-level entry, and even surviving reboots, permitting attackers to keep up management over contaminated hosts indefinitely. In response to Moonlock Lab, campaigns distributing Atomic have not too long ago shifted from broad distribution channels like cracked software program websites to focused phishing aimed toward cryptocurrency house owners and utilizing staged job interview invites to contaminate freelancers. The US, France, Italy, the UK, and Canada are among the many most affected by the stealer malware. It’s only the second recognized case of backdoor deployment at a worldwide scale focusing on macOS customers, after North Korea. “The improve to AMOS represents a major escalation in each functionality and intent, whether or not the modifications have been made by the unique malware authors or by another person modifying the code,” the corporate mentioned. “It is clear that the Russia-affiliated authors of Atomic macOS Stealer are following within the footsteps of North Korean assault teams.”
- Name of Responsibility Makers Takes Recreation Offline After Studies of RCE Exploit — The makers of Name of Responsibility: World Struggle 2 introduced that the PC model of the sport has been taken offline following “studies of a difficulty.” The difficulty seems to be a safety downside, particularly a distant code execution (RCE) vulnerability within the fashionable online game that might permit an attacker to take over others’ PCs throughout dwell multi-player matches. The RCE exploit has been discovered to be abused to open command prompts on sufferer PCs, ship mocking messages by way of Notepad, and forcibly shut down gamers’ computer systems, amongst others. Activision has not formally commented on the difficulty, however it’s mentioned to be working to remediate the bug.
- BaitTrap Makes use of Over 17K Websites to Push Scams — A community of greater than 17,000 web sites is mimicking trusted manufacturers, together with CNN, BBC and CNBC, to redirect guests to on-line scams. The BaitTrap community makes use of Google and Meta advertisements, social media posts, and YouTube movies to lure victims. The bogus websites usually gather private info and try and hijack on-line crypto accounts. They aim audiences in additional than 50 nations all around the globe. The websites publish faux tales that includes outstanding public figures, together with nationwide leaders and central financial institution governors, and falsely hyperlink these figures to “fabricated funding schemes to be able to construct belief and get engagement from victims.”
- Dutch Police Arrest 5 Phishing Gang Members — Dutch police have arrested 5 members of a phishing gang that operated out of town of Lelystad. 4 of the group’s members are youngsters aged 14 to 17. Authorities mentioned the suspects used QR codes despatched by way of e mail to gather login credentials for native banks. In a associated legislation enforcement improvement, Nepalese authorities have apprehended 52 individuals for allegedly operating on-line courting and crypto funding scams. The group ran a name heart and a courting app referred to as METOO to lure younger Nepali girls and facilitate fraudulent on-line transactions. Six of the detained suspects are Chinese language and are believed to have managed the operation.
- German Court docket Orders Meta to Pay €5K Over GDPR Violation — A German court docket has dominated that Meta should pay €5,000 ($5,900) to a German Fb person who sued the platform for embedding its Pixel monitoring expertise in third-party web sites. The ruling might open the door to giant fines down the highway over knowledge privateness violations regarding related monitoring instruments. The Regional Court docket of Leipzig in Germany dominated that Meta monitoring pixels and software program improvement kits embedded in numerous web sites and apps gather customers’ knowledge with out their consent and violate the continent’s Basic Information Safety Regulation (GDPR). “Each person is individually identifiable to Meta always as quickly as they go to the third-party web sites or use an app, even when they haven’t logged in by way of the Instagram and Fb account,” the court docket mentioned.
- LFI Flaw in Microsoft Export to PDF Characteristic — A Native File Inclusion (LFI) vulnerability has been disclosed in Microsoft 365’s Export to PDF performance, probably permitting attackers to entry delicate inner knowledge when changing HTML paperwork to PDF. The vulnerability, reported by safety researcher Gianluca Baldi, was subsequently patched by Microsoft, incomes them a $3,000 bounty reward. “It turned on the market was an undocumented habits that allowed changing from HTML to PDF recordsdata,” Baldi mentioned. “By embedding particular tags (
- Unpatched Flaws in Ruckus Wi-fi — A number of unpatched safety flaws have been disclosed (CVE-2025-44954, CVE-2025-44955, CVE-2025-44957, CVE-2025-44958, CVE-2025-44960, CVE-2025-44961, CVE-2025-44962, CVE-2025-44963, and CVE-2025-6243) in Ruckus Wi-fi administration merchandise Digital SmartZone (vSZ) and Community Director (RND) may very well be exploited by an attacker to leak delicate info and compromise the wi-fi setting. The issues embody authentication bypass, hard-coded secrets and techniques, arbitrary file learn by authenticated customers, and unauthenticated distant code execution. “An attacker with community entry to Ruckus Wi-fi vSZ can exploit CVE-2025-44954 to realize full administrator entry that may result in complete compromise of the vSZ wi-fi administration setting,” CERT/CC mentioned. “Moreover, a number of vulnerabilities could be chained to create chained assaults that may permit the attacker to mix assaults to bypass any safety controls that forestall solely particular assaults.” Noam Moshe of Claroty Team82 has been credited with discovering and reporting the problems. Within the absence of patches, customers are suggested to restrict entry to trusted customers and their authenticated purchasers to handle the infrastructure by way of a safe protocol like HTTPS or SSH.
- Safety Flaws in Gigabyte UEFI — A number of safety flaws have been disclosed in UEFI modules current in Gigabyte firmware (CVE-2025-7026, CVE-2025-7027, CVE-2025-7028, and CVE-2025-7029) that an attacker might exploit to raise privileges and execute arbitrary code within the System Administration Mode (SMM) setting of a UEFI-supported processor. “An attacker with native or distant administrative privileges could exploit these vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary code in System Administration Mode (Ring -2), bypassing OS-level protections,” CERT/CC mentioned. “These vulnerabilities could be triggered by way of SMI handlers from inside the working system, or in sure instances, throughout early boot phases, sleep states, or restoration modes – earlier than the OS absolutely masses.” Profitable exploitation of the vulnerabilities can disable UEFI safety mechanisms akin to Safe Boot and Intel BootGuard, facilitating stealthy firmware implants and chronic management over the system. The issues have been found and reported by Binarly.
- Android didn’t have a patch for the primary time in July 2025 in a Decade — Google introduced that no safety patches have been launched for Android and Pixel units for the month of July 2025, ending a decade-long streak of safety updates. That is the primary month no safety updates have been launched since Google began rolling out month-to-month Android fixes in August 2015.
- Indonesia Extradites Russian Nationwide for Promoting Private Information on Telegram — Indonesia has extradited a Russian citizen named Alexander Zverev for allegedly operating a Telegram channel that offered private knowledge obtained from legislation enforcement databases. Russian authorities claimed that Zverev operated an unnamed legal community between 2018 and 2021 that profited from promoting delicate private info sourced from databases belonging to Russia’s Inside Ministry (MVD), Federal Safety Service (FSB), and cell phone operators. Subscribers of the Telegram channel might allegedly buy particulars about Russian residents, together with personal info. Authorities haven’t disclosed the title of the channel or whether or not it’s at present operational.
- Legislation Enforcement Catches Up on Ransomware Actors — The Brussels legal court docket sentenced the Russian developer of Crylock ransomware to seven years in jail for masterminding the malware’s deployment on 1000’s of computer systems. His former co-conspirator, a feminine concerned in promoting Crylock and negotiating with the victims, was sentenced to 5 years. Greater than €60 million (~$70 million) in cryptocurrency representing unlawful proceeds from the ransomware operation have been seized by legislation enforcement. The event got here as French authorities arrested a 26-year-old Russian basketball participant for his alleged position in ransomware assaults. Daniil Kasatkin was arrested on June 21, 2025, on the Charles de Gaulle Airport in Paris on the request of U.S. authorities. It is alleged that Kasatkin helped an unnamed ransomware gang negotiate ransoms. Kasatkin’s lawyer denied the costs and claimed his shopper had no technical abilities. “He purchased a second-hand laptop. He did completely nothing. He is shocked,” his lawyer, Frédéric Bélot, informed AFP. “He is ineffective with computer systems and may’t even set up an software. He did not contact something on the pc: it was both hacked, or the hacker offered it to him to behave beneath the duvet of one other individual.” He is at present being held pending extradition to the U.S. The ransomware group Kasatkin was allegedly concerned with has not been named, however is alleged to have attacked roughly 900 firms. The U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) mentioned not too long ago that it is conscious of 900 organizations hit by the Play ransomware group.
- RansomedVC Returns After Hiatus; Leaks Medusa Information — The RansomedVC ransomware group has returned after a two-year absence and leaked the inner chat transcripts of the Medusa ransomware group from December 11, 2022, to March 2023. RansomedVC claimed Medusa’s admin “appears fully absent and unresponsive to the wants of his members” and indicated that they could both be making an attempt an exit rip-off or may need been compromised by legislation enforcement. “From the transcript and analyzing earlier occasions, the group is principally targeted on focusing on Fortinet Entry as an SQLi Vulnerability was exploited by the group in 2024 and the present leaked chat that mentions ‘Forti’ additionally underlines its significance which dates again to 2023,” safety researcher Rakesh Krishnan mentioned. The event coincides with the emergence of recent gamers, together with BERT. One other ransomware group, SafePay, which emerged final yr has since advanced to turn into “one of the crucial lively and harmful actors,” primarily focusing on managed service suppliers (MSPs) and small-to-midsize companies (SMBs). “The group makes use of traditional however efficient strategies: RDP- and VPN-based intrusion, credential theft, privilege escalation and living-off-the-land binaries to quietly transfer by sufferer networks, exfiltrate delicate knowledge after which encrypt recordsdata,” Acronis mentioned. Ransomware assaults on companies world wide have elevated by 213% within the first quarter of 2025, with 2,314 victims reported over 74 distinct knowledge breach websites, in comparison with simply 1,086 within the first quarter of 2024.
- Disgruntled IT Employee Jailed for Cyber Assault — Mohammed Umar Taj, 31, of Hyrst Garth, Batley, U.Ok., was sentenced to seven months and 14 days in jail for unlawfully accessing his former employer’s premises, altering login credentials, and altering entry credentials and multi-factor authentication configuration to disrupt the corporate’s operations. He was suspended from work in July 2022.
- Hacker Behind GMX Change Returns Belongings — An unknown hacker behind the $42 million theft from decentralized trade GMX has returned the stolen property in return for a $5 million bug bounty. The event occurred after GMX promised to not pursue prices if the hacker returned the funds. In a autopsy report, the corporate mentioned it has addressed the foundation trigger in a subsequent replace. “Based mostly on a assessment of the incident by contributors, auditors and safety researchers, the foundation reason behind the exploit is a reentrancy assault,” it mentioned. “By using this reentrancy and bypassing the common quick value calculations, the attacker was capable of open positions and manipulate the common quick value for BTC downwards from the preliminary worth of $109,505.77 to $1,913.70.”
- Flaws in Thermomix TM5 Equipment — A safety evaluation of Thermomix TM5’s has uncovered a number of weaknesses that might render the kitchen equipment prone to firmware downgrade assaults (restricted to variations previous to 2.14. Model 2.14) and safe boot bypass, permitting an attacker to realize persistence. “This vulnerability could be chained with the firmware downgrade vulnerability to realize arbitrary code execution and apply a managed firmware replace file with out messing up with the NAND flash,” Synacktiv mentioned. “By exploiting these flaws, one can alter the firmware model block to bypass anti-downgrade protections, downgrade the firmware, and probably execute arbitrary code.”
- API Shopper Safety Dangers Detailed — An evaluation of API purchasers like Postman, Insomnia, Bruno, and Hoppscotch has uncovered potential vulnerabilities inside their JavaScript sandboxing implementations that may very well be exploited to attain code execution. “Working untrusted code with none isolation is, after all, a foul concept, however it is usually problematic to make use of seemingly working options akin to Node.js’s built-in vm module or the third-party vm2 bundle,” Sonar researchers Oskar Zeino-Mahmalat and Paul Gerste mentioned. “These are recognized to have bypasses that permit malicious code escape the sandbox and get entry to system assets.”
- Ubuntu Turns Off Intel GPU Safety Mitigations — Ubuntu has disabled a safety characteristic that protected Intel GPUs towards Spectre side-channel assaults. Canonical mentioned it now makes use of kernel-level protections, making it not essential to have these safeguards. Ubuntu builders can count on the working system to see a 20% in enchancment in efficiency following the replace. “After dialogue between Intel and Canonical’s safety groups, we’re in settlement that Spectre not must be mitigated for the GPU on the Compute Runtime degree,” Ubuntu maintainers mentioned. “At this level, Spectre has been mitigated within the kernel, and a transparent warning from the Compute Runtime construct serves as a notification for these operating modified kernels with out these patches. For these causes, we really feel that Spectre mitigations in Compute Runtime not provide sufficient safety influence to justify the present efficiency tradeoff.”
- Botnet Engages in Internet Scraping — A brand new botnet comprising greater than 3,600 distinctive IP addresses has been noticed concerned in internet scraping exercise a minimum of since April 19, 2025. The vast majority of the botnet’s contaminated hosts are situated in Taiwan, Japan, Bulgaria, and France, GreyNoise mentioned, with focused methods predominantly situated in the US and United Kingdom. “The dominance of Taiwanese IP house might counsel: A standard expertise or service deployed extensively in Taiwan has been compromised, or that native publicity to a shared vulnerability is driving the clustering,” the risk intelligence agency mentioned.
- Czechia Turns into the Newest Nation to Situation Warning About DeepSeek — Czechia’s cybersecurity company, the Nationwide Cyber and Data Safety Company (NÚKIB), issued a proper warning detailing the nationwide safety dangers posed by means of software program supplied by Chinese language synthetic intelligence firm DeepSeek. “The first safety considerations stem from inadequate safety of information transmission and dealing with, from the gathering of information varieties which, in higher quantity, could result in person deanonymization, and lastly, from the authorized and political setting of the Folks’s Republic of China to which the corporate DeepSeek is absolutely topic,” NÚKIB mentioned. To that finish, the federal government has banned the usage of DeepSeek on state-owned units, urging the general public to be aware of the knowledge shared with the platform. Nonetheless, NÚKIB famous that the choice doesn’t apply to open-source giant language fashions (LLMs) developed by the corporate DeepSeek, supplied that their supply code is made obtainable for assessment and could be deployed regionally with none contact with servers related to DeepSeek or its associated entities. A number of different nations, together with Canada, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, South Korea, and Taiwan, have issued related warnings.
- TikTok Comes Underneath E.U. Radar Once more — Eire’s Information Safety Fee (DPC) mentioned it is opening a probe into TikTok over the switch of person knowledge within the European Union to servers situated in China. “The aim of the inquiry is to find out whether or not TikTok has complied with its related obligations beneath the GDPR within the context of the transfers now at problem, together with the lawfulness of the transfers [under GDPR],” the DPC mentioned. The event comes a little bit greater than two months after the DPC fined TikTok €530 million ($620 million) for infringing knowledge safety rules within the area by transferring European customers’ knowledge to China and for permitting TikTok’s China-based employees entry European person knowledge. TikTok, which is owned by China’s ByteDance, has been the topic of intense scrutiny on either side of the Atlantic over the way it handles private person info amid considerations that it poses a nationwide safety danger. As per stringent knowledge safety legal guidelines within the area, European person knowledge can solely be transferred exterior of the bloc if there are safeguards in place to make sure the identical degree of safety. TikTok can be dealing with the warmth in the UK after the First-tier Tribunal dominated that the Data Commissioner’s Workplace (ICO), the British knowledge regulator, has the ability to problem a financial penalty discover (MPN) to TikTok. The ICO fined TikTok £12.7 million in 2023, however the firm argued that “its processing was for creative functions, so the ‘particular functions’ provisions utilized.”
- Google Particulars Superior Safety in Android — Again in Could 2025, Google launched Superior Safety, a safety characteristic that “ensures all of Android’s highest security measures are enabled and are seamlessly working collectively to safeguard you towards on-line assaults, dangerous apps, and knowledge dangers.” Just like Lockdown Mode in Apple iOS, iPadOS, and macOS units, Superior Safety goals to supply improved guardrails for journalists and different high-risk targets. In Google Chrome, this consists of all the time utilizing safe connections, full website isolation on cellular units with 4GB+ RAM to maintain malicious websites away from respectable websites, and disabling JavaScript optimizations.
- SatanLock Declares Abrupt Shutdown — SatanLock, a more moderen ransomware group on the risk panorama, has introduced that it will likely be shutting down. The precise causes behind the sudden transfer is unclear. The group first emerged in early April, and printed 67 victims inside a span of a month. Nonetheless, Examine Level discovered that 65% of those victims had already been listed by different ransomware teams.
- Russia Rejects Legislation to Legalize White-Hat Hacking — Russia’s State Duma has rejected laws that might have legalized moral hacking, citing nationwide safety considerations. Politicians expressed worries that discovering vulnerabilities present in software program made by firms headquartered in hostile nations would require sharing them, which, in flip, might result in these nations abusing the defects for strategic acquire, native media reported.
- GitHub Repos Used to Distribute Malware as Free VPN — Risk actors have been noticed utilizing GitHub as a mechanism for staging stealer malware like Lumma by disguising it as ‘Free VPN for PC and Minecraft Pores and skin Changer. “The evaluation of the ‘Free-VPN-For-PC’ pattern revealed that, behind its seemingly respectable facade, it capabilities as a complicated malware dropper designed to implant the Lumma Stealer,” CYFIRMA mentioned. “Disguised as a useful instrument, the dropper makes use of a number of layers of obfuscation, in-memory execution, and course of injection to evade detection. The identical malware was additionally repackaged beneath the title ‘Minecraft Pores and skin,’ indicating a broader social engineering tactic focusing on totally different person pursuits.”
- NFC-Enabled Fraud Targets Philippines’ Monetary Sector — Chinese language cellular malware syndicates that depend on NFC relay assaults have now unfold to the Philippines, Resecurity revealed. “Main underground outlets managed by Chinese language cybercriminals checklist the Philippines as one of the crucial impacted areas, primarily based on the amount of compromised bank cards (CCs),” the corporate mentioned. A few of the different high areas focused by Chinese language cybercriminals embody Australia, Taiwan, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Hong Kong, Korea, and Indonesia. These teams, lively on Telegram, allow fraudsters to accumulate compromised playing cards and in addition test whether or not they’re legitimate or not, utilizing micro-charges carried out by way of fraudulent retailers arrange by Chinese language cybercriminals. Attackers can then use instruments like Z-NFC, X-NFC, SuperCard X, Track2NFC to clone stolen card knowledge and carry out unauthorized transactions utilizing NFC-enabled units.
- GitPhish Device to Automate GitHub System Code Phishing — Cybersecurity researchers have demonstrated a novel preliminary entry vector that leverages the OAuth 2.0 System Authorization Grant circulation to compromise a company’s GitHub repositories and software program provide chain. Referred to as System Code Phishing, the method employs social engineering ploys to trick targets into coming into an eight-digit machine code by clicking on an attacker-provided hyperlink, probably main to finish compromise of organizational GitHub repositories and software program provide chains. It is value noting that machine code phishing has been utilized by suspected Russian risk actors to realize entry to Microsoft accounts. “We designed GitPhish explicitly for safety groups trying to conduct assessments and construct detection capabilities round System Code Phishing in GitHub,” Praetorian mentioned. “Crimson teamers can simulate sensible assault situations to check organizational resilience, whereas detection engineers can validate their potential to determine suspicious OAuth flows, uncommon GitHub authentication patterns, and potential social engineering makes an attempt.”
- Malicious Browser Extensions Galore — A set of 18 malicious extensions with 2.3 million downloads in Google’s Chrome Internet Retailer and Microsoft Edge Addons have been discovered to include options to trace customers’ website visits, steal browser exercise, and redirect to probably unsafe websites. These add-ons pose as productiveness and leisure instruments throughout numerous classes, together with shade pickers, emoji keyboards, climate forecasts, video velocity controllers, VPN proxies for Discord and TikTok, darkish themes, quantity boosters and YouTube unblockers. Whereas they provide the marketed performance, they supply the right cowl to hide their browser surveillance and hijacking capabilities. The exercise has been codenamed RedDirection by Koi Safety. What makes the marketing campaign regarding is that the extensions began off as benign instruments, with the malicious code launched at a later time by way of updates, in some instances after years. Final month, LayerX revealed that it had recognized a community of malicious “sleeper agent” extensions which are probably being arrange as a stepping stone for future exercise. These extensions have been recognized as being put in practically 1.5 million occasions. One of many extensions that is frequent to each these clusters is “Quantity Max — Final Sound Booster” (extension ID: mgbhdehiapbjamfgekfpebmhmnmcmemg). The disclosure coincides with one other marketing campaign uncovered by Safe Annex dubbed Mellow Drama, which has reworked a whole bunch of extensions incorporating a Mellowtel library right into a distributed internet scraping community. The extensions have been collectively put in practically 1 million occasions. “We found a brand new monetization library developed by Mellowtel that pays extension builders in trade for the ‘unused bandwidth’ of customers who’ve an extension put in,” John Tuckner mentioned. The library has been traced again to a person named Arslan Ali, who can be the founding father of an organization referred to as Olostep that claims to supply the “world’s Most Dependable and Price-effective Internet Scraping API.” It is believed that scraping requests from Olostep are distributed to any of the lively extensions which are operating the Mellowtel library. Mellowtel has since responded, stating it doesn’t gather or promote customers’ private knowledge. “As an alternative of gathering customers’ knowledge, monitoring them throughout the online, and displaying them advertisements continuous, we’re constructing a monetization engine for builders primarily based on bandwidth/useful resource sharing,” Ali mentioned.
🎥 Cybersecurity Webinars
- Cease ‘Pip Set up and Pray’: Easy methods to Safe Your Python Provide Chain in 2025 – Repojacking, typosquatting, and poisoned containers are turning trusted instruments into assault vectors. Whether or not you are managing infrastructure or writing code, securing your Python setting is not elective. Discover ways to take management earlier than attackers do.
- From Login Fatigue to AI Fatigue: Securing Id in 2025 – AI is streamlining logins—however it’s additionally elevating alarm bells. Clients are rising cautious of how their knowledge is used, and belief is turning into tougher to earn. This webinar reveals how main manufacturers are rebuilding digital belief whereas staying safe and user-friendly.
- From Copilots to Assault Bots: Securing the AI Id Layer – As AI copilots and brokers go mainstream, attackers are utilizing the identical instruments to bypass logins, impersonate customers, and exploit APIs. On this webinar, Okta reveals the way to outpace AI threats by making identification your first—and final—line of protection.
🔧 Cybersecurity Instruments
- BitChat – It’s a instrument that allows you to chat with out the web, servers, and even telephone numbers—simply Bluetooth. It builds a neighborhood mesh community between close by units, enabling absolutely offline communication. Public group chats are safe and able to use. Personal messages and channels are nonetheless beneath improvement and have not been externally reviewed, so they don’t seem to be advisable for delicate conversations simply but.
- GitPhish – It’s a instrument for testing GitHub’s machine login circulation in a safety analysis setting. It helps stimulate phishing-style assaults by creating faux login pages, capturing tokens, and monitoring exercise. Constructed for moral testing, it features a dashboard, automated deployments, and logging—all meant to be used in secure, approved environments solely.
Disclaimer: These newly launched instruments are for academic use solely and have not been absolutely audited. Use at your individual danger—assessment the code, check safely, and apply correct safeguards.
🔒 Tip of the Week
Map Identified Vulnerabilities Robotically Throughout Your Stack — Manually checking for CVEs is sluggish, incomplete, and simple to get improper. As an alternative, use automated instruments that correlate software program variations with recognized vulnerabilities throughout your total setting—each inner and internet-facing.
Begin with Nmap and instruments like CVEScannerV2 or Vulners NSE to scan dwell companies for uncovered software program variations and match them to CVE databases. For deeper insights:
- Use instruments like Nuclei (customizable vulnerability templates), Trivy (container + system CVEs), and Grype (SBOM-based scanning).
- Monitor third-party parts with OSV-Scanner or Dependency-Monitor when you’re constructing software program.
- Arrange scheduled scans and use instruments that combine with ticketing methods to make sure groups truly act on the findings.
Lastly, filter out noise—not each CVE is value patching. Give attention to CVEs with public exploits, excessive CVSS scores, and publicity to customers or attackers.
Professional tip: All the time validate findings with real-world exploitability, not simply model matches.
Conclusion
What stands out this week is not simply the size of incidents—it is how acquainted instruments, platforms, and even browser extensions are being quietly turned towards us. From purple teaming software program reappearing as malware loaders to code libraries enabling stealth assaults, the road between respectable use and exploitation retains getting tougher to see. When trusted environments turn into a part of the assault chain, safety groups should look past patching and begin questioning assumptions about what’s secure by default.
Staying forward means paying simply as a lot consideration to what’s already contained in the gates as what’s making an attempt to interrupt in.

